Advanced Oxidation Process for Wastewater Treatment Using H2O2 and UV Method
Main Article Content
Abstract
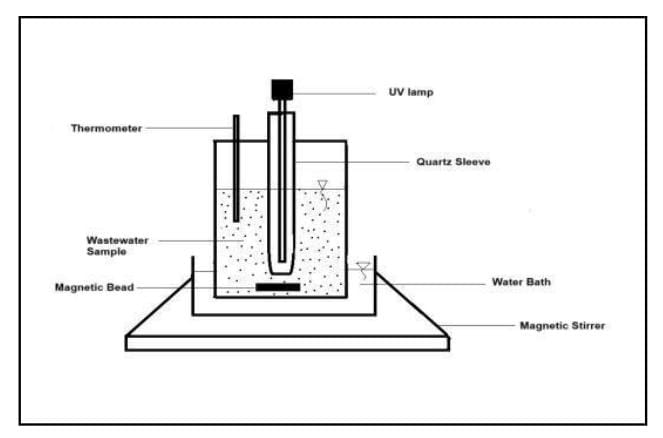
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) are being identified as potential technologies for wastewater treatment and improvement of conventional biological treatment processes, especially for wastewater with highly toxic and poorly biodegradable organic compounds. In the present work, wastewater samples were obtained from Kala Odha in Ichalkaranji. Several parameters of the wastewater, such as pH, turbidity, total dissolved solids (TDS), total suspended solids (TSS), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total Kjeldahl nitrogen (TKN), total phosphorus, and total alkalinity, were determined by standard methods. The best dose of hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) and the best treatment time were established by using a photochemical reactor in batch mode. The research revealed that the highest COD removal efficiency of 74.41% was obtained with a concentration of 300 mg/L of H₂O₂ after a reaction time of 90 minutes, from an initial COD of 1720 mg/L.To further optimize the treatment process, COD tests were also performed at different time intervals. The results showed that a reaction time of 75 minutes produced the maximum COD removal efficiency of 76.27% at the optimum dose of 300 mg/L of H₂O₂ with an initial COD of 2360 mg/L. Based on the findings, it is clear that the combined application of H₂O₂ and UV methods is a promising solution for efficient removal of COD from wastewater.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.