Classification of Overlapping Red Blood Cells in Microscopic Blood Smear Images Using Deep Learning
Main Article Content
Abstract
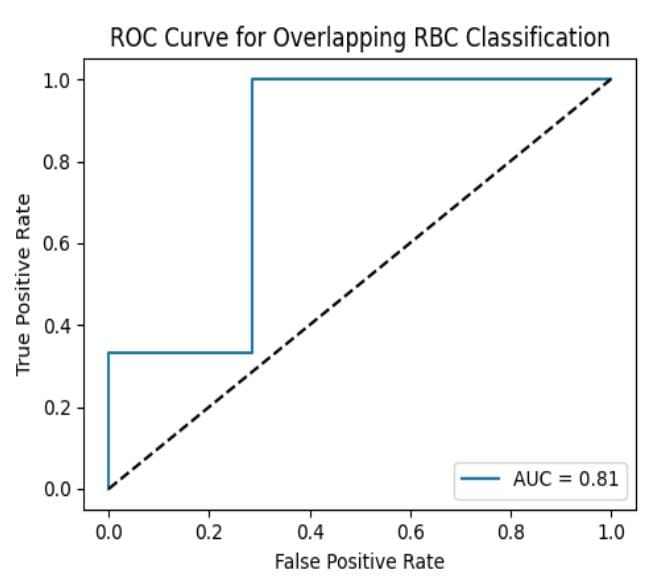
Automated analysis of microscopic blood smear images plays a crucial role in modern hematological diagnosis. While existing computer vision and deep learning techniques have demonstrated strong performance in detecting and counting isolated blood cells, the classification of overlapping red blood cells (RBCs) remains a challenging problem due to ambiguous boundaries and dense cellular arrangements. Traditional image processing methods often fail under such conditions, leading to inaccurate cell counts and potential diagnostic errors. In this work, a deep learning–based framework for the classification of overlapping and non-overlapping red blood cells is presented. A real microscopic dataset derived from the publicly available Blood Cell Count Dataset (BCCD) is utilized. Red blood cell regions are first localized using a pretrained YOLO-based object detector, followed by a lightweight convolutional neural network for binary classification of overlapping and single RBCs. Weak supervision based on morphological area estimation is employed to generate overlap labels. Experimental evaluation on a dataset of 38 RBC samples demonstrates an overall classification accuracy of up to 80%, with strong recall for single RBCs and moderate performance for overlapping cases. The results highlight both the effectiveness and the inherent challenges of overlapping RBC classification in small and weakly supervised datasets, providing a foundation for future improvements using larger datasets and pixel-level annotations.