Machine Learning Model for Efficient Botnet Attack Detection and Classification
Main Article Content
Abstract
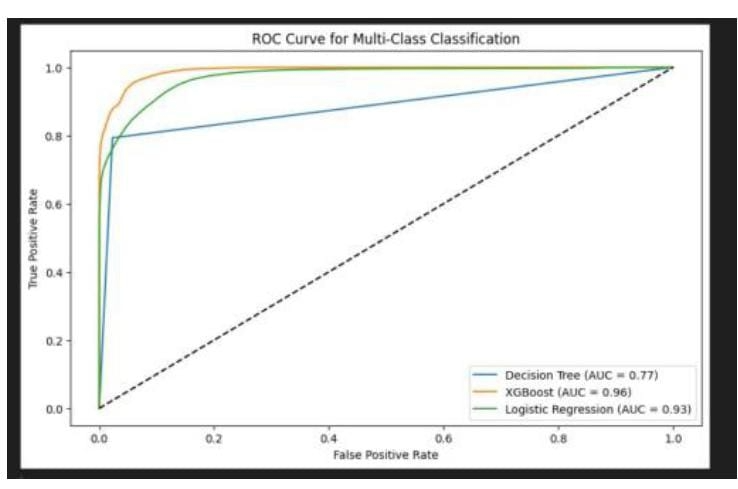
Botnets constitute a significant threat to cybersecu- rity, enabling large-scale malicious operations such as distributed denial-of-service attacks, data exfiltration, and unauthorized system access. This research presents a machine learning-based framework for the detection and classification of botnet attacks, utilizing Decision Tree, XGBoost, and Logistic Regression al- gorithms. The UNSW-NB15 dataset is employed, with distinct training and testing splits to ensure model generalization and to prevent overfitting. Feature selection techniques are applied to en- hance model performance and reduce computational complexity. Model evaluation is conducted using confusion matrices and Re- ceiver Operating Characteristic–Area Under Curve (ROC-AUC) metrics to provide a comprehensive assessment. Experimental results indicate that ensemble methods, particularly XGBoost, deliver superior performance in accurately detecting and cate- gorizing botnet traffic across various attack types. The findings highlight the effectiveness of machine learning approaches in improving the robustness and scalability of network intrusion detection systems.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.