Evaluation of Artificial Intelligence in Answering Dermatological Medical Questions
Main Article Content
Abstract
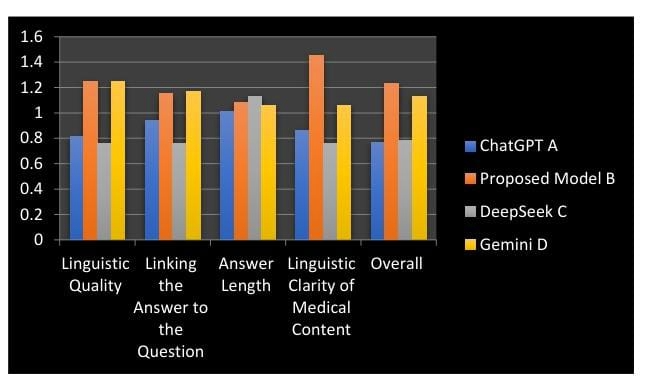
This research presents a systematic evaluation of the adaptation of a large Arabic linguistic model (based on AraGPT2) to answer questions in the field of dermatology. The study aims to bridge the gap in specialized linguistic resources by fine-tuning the model to a newly created and purified dataset, collected using a hybrid methodology combining web scraping and filtered data enrichment. This dataset consists of 40,132 specialized question-answer pairs. The performance of the finely tuned model was quantitatively assessed using BERTScore, BLEU, Levenshtein distance, and two types of initial human evaluation. The quantitative results showed strong semantic performance, with the model achieving a BERTScore (F1) of 64.49%, confirming its ability to effectively understand medical context and meaning. In contrast, the verbal matching measures reflected a tendency toward free generation, scoring BLEU at 10.00% and Levenshtein distance at 28.13%. These results demonstrate that the model favors the free generation of new formulations over the verbatim retrieval of reference texts. Furthermore, the qualitative results of the proposed model showed a competitive overall performance of 4.01, achieving a high score of 4.55 in the criteria of linguistic clarity and readability for non-expert audiences. These results confirm that the model's primary contribution lies in its ability to enhance human comprehension (understanding) of complex medical data. The study also underscores the urgent need for subsequent clinical validation by field experts to ensure complete clinical accuracy and reliability.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.