A Machine Learning–Driven Framework for Predicting Nutritional Deficiencies using a Multi-Data Approach
Main Article Content
Abstract
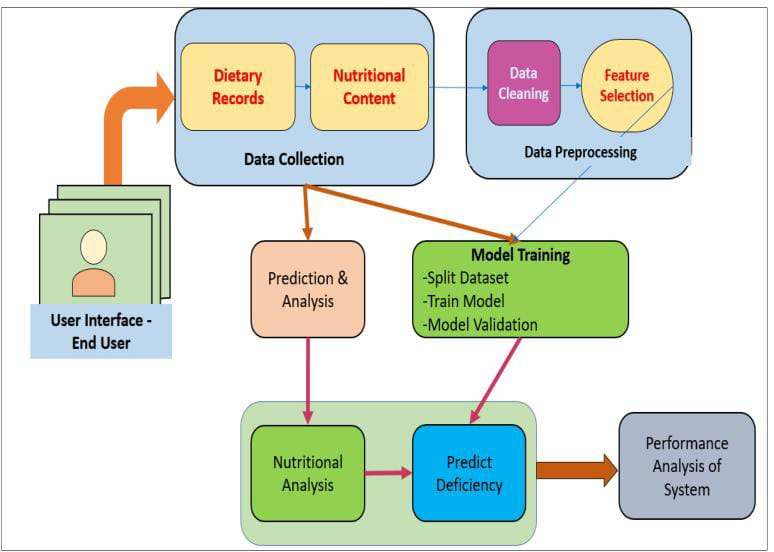
Nutritional deficits are still a major health problem around the world, and bad eating habits can make them worse. Self-reporting errors and subjective biases make it hard to use traditional methods to figure out what people are eating and predict if they are deficient. The purpose of this study is to look into how machine learning (ML) algorithms can be used to better predict nutritional deficiencies from eating habits. We look into several machine learning methods, such as controlled learning algorithms (like decision trees, random forests, and support vector machines), unsupervised learning algorithms (like clustering algorithms), and advanced deep learning models (like convolutional and recurrent neural networks). To make deficiency estimates more accurate and give more personalized dietary advice, we are looking at big sets of data on what people eat, their demographics, and their health records. Our findings show that machine learning algorithms, especially deep learning models, can successfully record complex patterns and temporal variations in dietary data, which leads to better prediction accuracy. Combining machine learning with wearable tech and mobile apps makes tracking and stepping in even easier in real time. Using machine learning to predict nutritional deficiencies is a big step forward in personalized nutrition, even though there are some problems, like poor data quality and privacy issues. It can help with both public health and managing one's own diet.