TweetScan: An Intelligent Framework for Deepfake Tweet Detection Using CNN and FastText
Main Article Content
Abstract
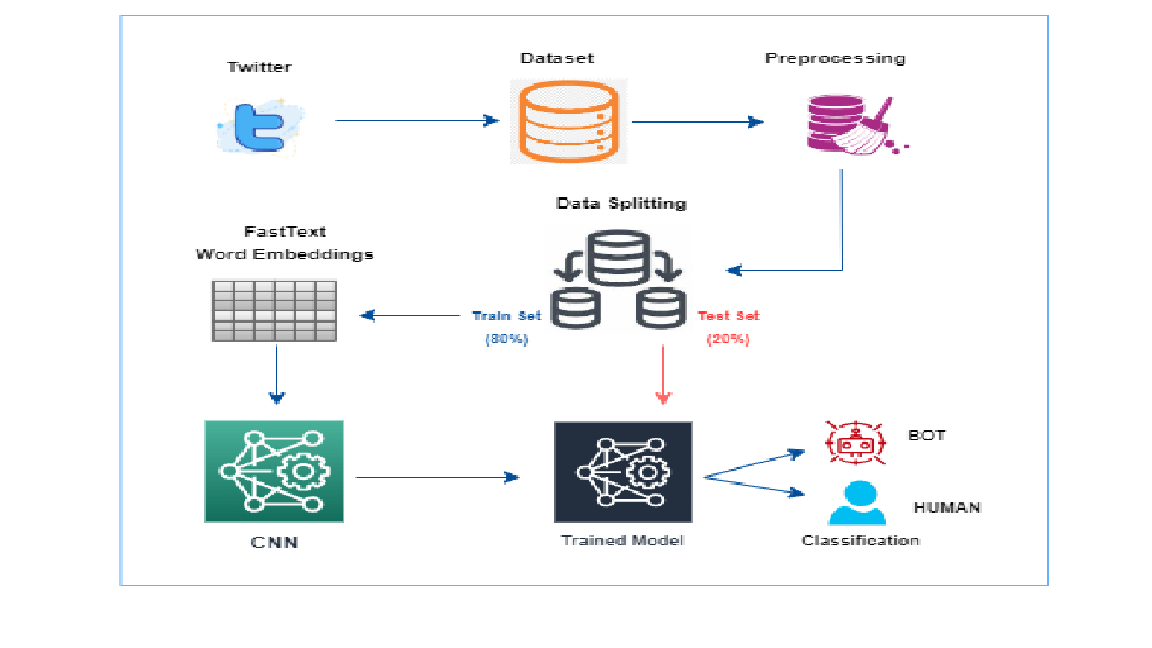
With the widespread influence of social media platforms, the rapid dissemination of information—both authentic and deceptive—has become a major concern. One of the growing threats is the use of automated bots to spread deepfake or machine-generated tweets that mimic human-written content. These bots can manipulate public opinion, spread misinformation, and affect real-world events. To address this issue, this paper proposes a deep learning-based system for detecting deepfake tweets using FastText embeddings and various classification algorithms. A detailed performance comparison is conducted between traditional machine learning classifiers (Naïve Bayes, Logistic Regression, Decision Tree, Random Forest) and deep learning models such as CNN and LSTM. Among all models, CNN outperformed others in terms of accuracy and robustness. Furthermore, a hybrid model combining CNN feature extraction with Random Forest classification was introduced, achieving even higher performance. The system uses the publicly available “TweepFake” dataset and includes modules for dataset preprocessing, embedding, training, and real-time tweet prediction. The proposed solution effectively distinguishes between tweets authored by humans and bots, offering a valuable tool to combat social media-based misinformation.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.