An Eye-Tracking-Based Adaptive Framework for Dyslexia Support
Main Article Content
Abstract
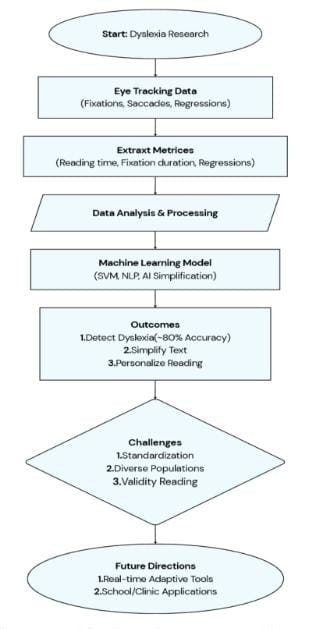
Worldwide, dyslexia is estimated to affect about 10% of the global population, which translates to approximately 700 to 780 million people living with dyslexia. Dyslexia is a learning disability that can make reading, spelling, and word recognition more difficult. Dyslexic readers may find it difficult to navigate the dense, static text blocks on online learning platforms. To aid dyslexic individuals in reading online content, an eye-tracking-enabled website has been developed. This website dynamically adjusts to each reader in real time, personalizing the reading experience by enlarging, spacing-out letters for challenging words, making the reading experience highly tailored and supportive for dyslexic readers. In this work WebGazer.js framework tracks the eyesight, and React.js, JavaScript and Tailwind CSS make it browser independent. Usability testing revealed that adjusting word spacing and responding to a reader’s eye movements greatly enhanced readability, focus and overall comfort for people with dyslexia.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.