A Thorough Literature Review on Automatic Speaker Diarization Employing Machine Learning and Deep Learning Methodologies
Main Article Content
Abstract
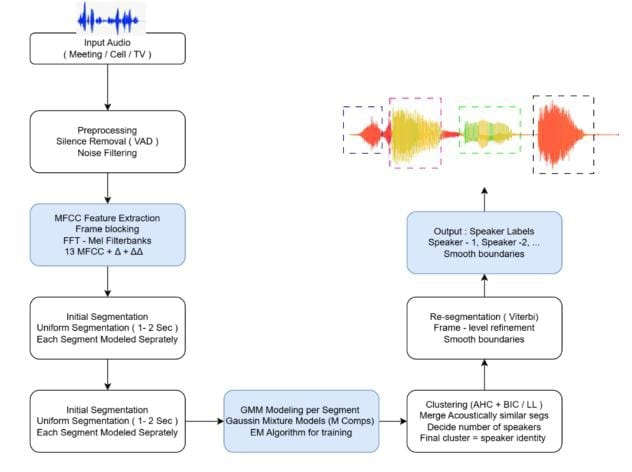
Automatic Speaker Diarization (ASD) is the process of dividing an audio recording into regions where each speaker is the same and figuring out "who spoke when" with-out knowing who the speakers are ahead of time. It is a necessary part of meeting transcription, conversational analytics, indexing for broadcast media, forensic audio processing, call-center monitoring, and modern systems for human-computer interac-tion. In the past twenty years, diarization research has moved from traditional statis-tical models like Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) based on MFCCs and Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) segmentation to more advanced representation learning methods like i-vectors and Probabilistic Linear Discriminant Analysis (PLDA). Later advances in deep learning led to strong neural embeddings like x-vectors and ECAPA-TDNN, which made it much easier to identify speakers in difficult sound situations. The most current Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) models, such as Wav2Vec 2.0, HuBERT, and WavLM, have set new standards by learning strong speech representations without any labeled input. End-to-End Neural Diarization (EEND), UIS-RNN, and VB-HMM re-segmentation are some of the complementary methods that have improved how well we can handle overlaps and refine time.
This evaluation offers a thorough examination of recent advancements, evaluat-ing the advantages and disadvantages of prominent diarization methodologies, pin-pointing enduring research deficiencies, and delineating prospective avenues for the enhancement of precise, multilingual, and real-time speaker diarization systems.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.