NeuroVibe – Neural Vibration Pathway for Deaf Users
Main Article Content
Abstract
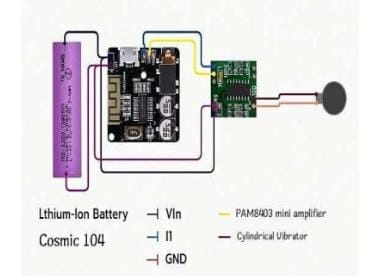
People with hearing impairments often feel like they cannot sense the sound from their surroundings. NeuroVibe is an innovative wearable device that provides an alternative way of perceiving sound through bone conduction-based vibrotactile feedback; it transforms the sound frequencies into gentle mechanical vibrations that can easily be perceived via teeth. The device consists of a Bluetooth audio module (Cosmic 104), a mini audio amplifier (PAM8403), a cylindrical vibration motor, a 3.7 V/1800 mAh rechargeable lithium battery, connecting wires, and a protective enclosure. When connected with an audio source, NeuroVibe converts sound frequencies into proportional intensities of vibration that reach the cochlea through the jawbone, enabling the user to feel rather than hear the sound sensation.
This work presents the design of the device, its working mechanism, and its vibration response for alphabetic sound patterns in the 3–7 kHz, frequency range. The results clearly indicate a relationship between frequency and vibration strength, thus pointing out NeuroVibe’s potential for being an affordable and effective assistive technology in people with partial or profound hearing loss.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.