Comparison of Machine Learning Models for Hand Sign Recognition
Main Article Content
Abstract
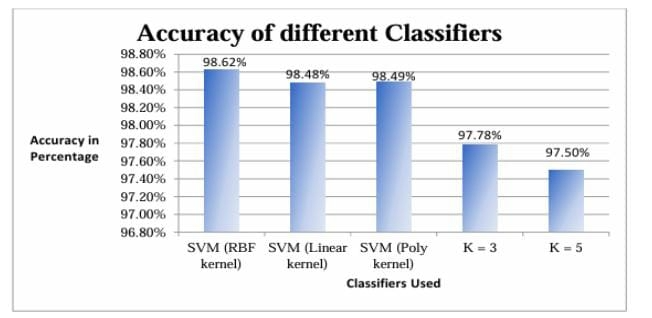
Hand sign recognition plays a crucial role in the development of assistive technologies for human–computer interaction and communication support for persons with hearing and speech impairments. This paper presents a comparative study of machine learning models for static hand sign recognition using a publicly available Indian Sign Language (ISL) dataset downloaded from Kaggle. A unified preprocessing pipeline was applied to all images, followed by extraction of three complementary feature sets: Hu Moments for capturing global shape properties, contour-based shape features for structural hand geometry, and Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG) for local gradient-based texture information. These features were combined into a single feature vector and used to train two major classifier families: K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) with different values of k, and Support Vector Machines (SVM) with multiple kernels, including Linear, Polynomial, and Radial Basis Function (RBF). The performance of each model was evaluated using accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score to identify the most effective classifier for multi-class hand sign recognition. Experimental results show that SVM with the RBF kernel consistently achieves superior classification accuracy compared to KNN and other SVM variants, demonstrating its suitability for high-dimensional feature representations in hand gesture recognition systems. The findings provide useful insights for selecting efficient machine learning models for real-time sign recognition applications.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.