IoT-Enabled Machine Learning for Water Quality Monitoring
Main Article Content
Abstract
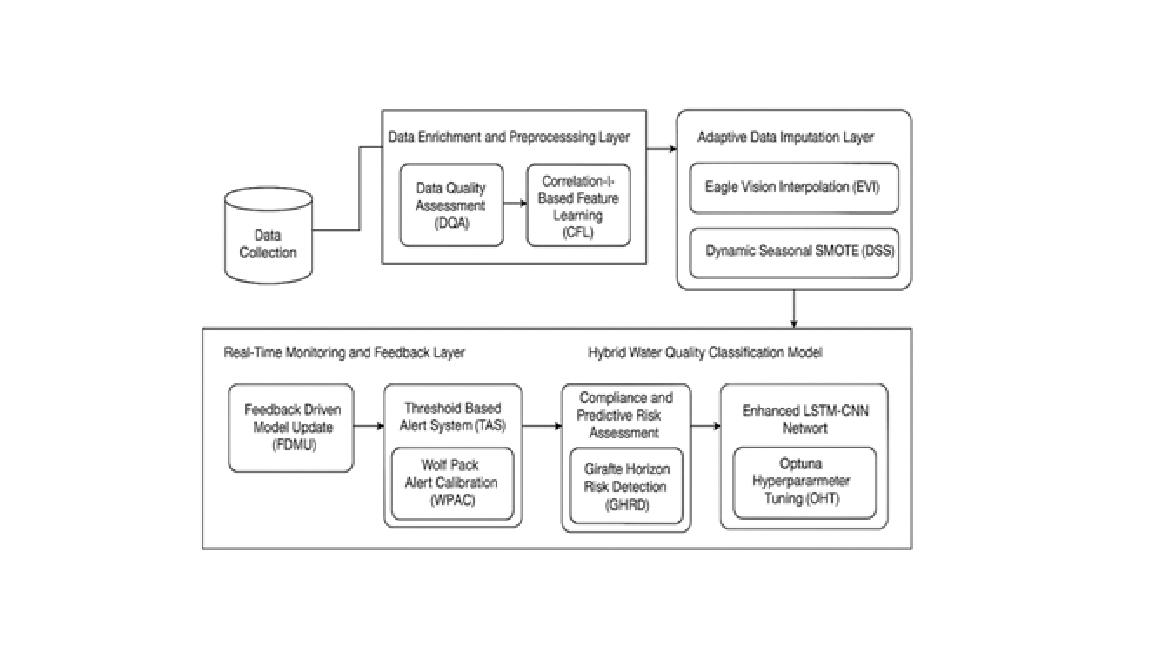
Determining water quality is most paramount concerning environmental sustainability and human health. By the time pollution of water becomes really bad, the traditional methods have kidnapped the entire spotlight, with sporadic sample collections and laboratory analyses, and these approaches fail to quantify the complexity and the changing nature of modern water pollution. This study presents an advanced machine learning framework integrated with Internet-of-Things (IoT) technology to enable real-time classification of water quality as per the standards of the Central Pollution Control Board-CPCB. Two novel techniques were introduced to overcome the challenges of "data integrity" and "imbalance": handling missing data through Eagle Vision Interpolation (EVI) and rebalancing skewed datasets through Dynamic Seasonal SMOTE (DSS). After developing a hybrid deep learning model combining Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), parameters of the hybrid deep learning model were optimized as per Optuna's hyperparameter tuning framework in order to enhance accuracy and robustness. Giraffe Horizon Risk Detection (GHRD) mechanisms are effectively proposed for continuous assessment of the regulatory compliance and threat detection mechanism. Moreover, a new system-A-Wolf Pack Alert Calibration (WPAC)-is organized to allow the dynamic classification as well as prioritization of water quality alerts. Another contribution of this work is the Bidirectional LSTM-based model which predicts pollution trends for early warning applications that lead to timely preventive measures. The proposed system demonstrates 94.49% impressive accuracy, indicating its efficacy for real-time monitoring, compliance assessment, and predictive intervention. A unique integration between conventional monitoring methods and intelligent decision-making engenders comprehensive management of water resources and public health security.