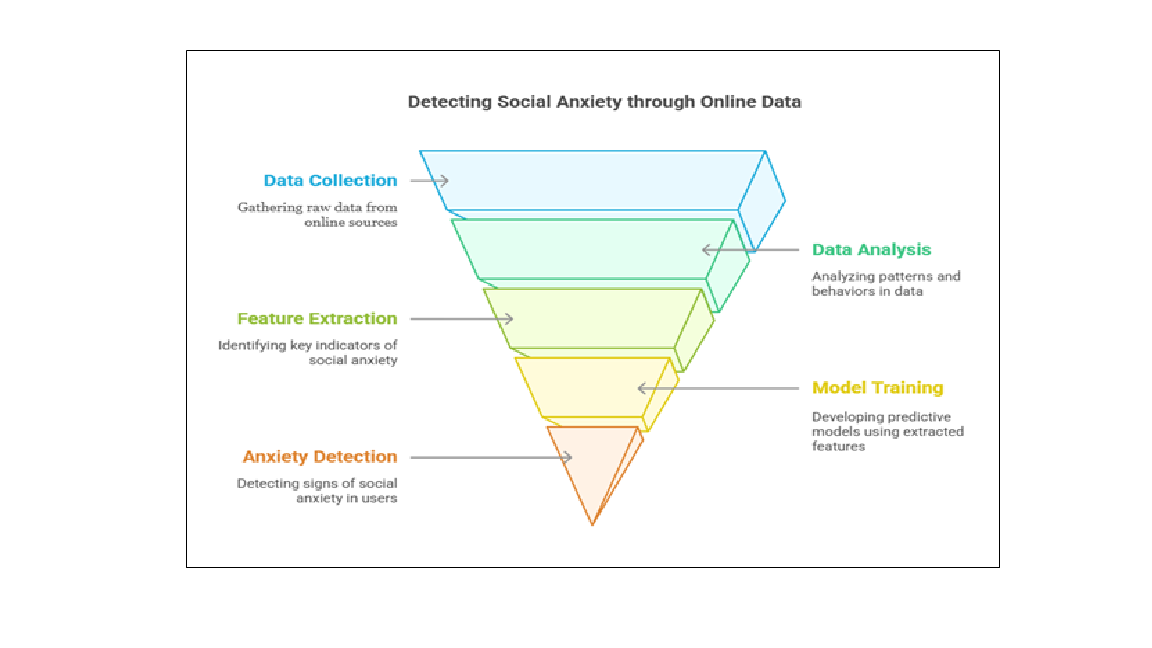
Detecting Social Anxiety with Online Social Network Data
Main Article Content
Abstract
Adolescents and young adults extensively use social media to maintain their relationships. Recent research indicates that those with high social anxiety often find it easier to communicate online. However, there is limited understanding of how certain characteristics of social media might help reduce the distress they experience in face-to-face interactions. This study draws on the Transformation Framework, which suggests that social media, with its unique features, can alter social relationships by facilitating emotional expression and online communication. These effects may vary between individuals who have social anxiety and those who do not. The use of social media was linked to increased symptoms of depression, social anxiety, appearance anxiety, and concerns related to appearance. Both general and appearance-related preoccupations showed distinct positive correlations with symptoms of depression and social anxiety, as well as with sensitivities about appearance. Additionally, preoccupation with appearance was found to amplify the connection between time spent on social media and concerns related to appearance.