Lightweight Hybrid Deep Learning and Machine Learning Framework for Multiclass Alzheimer’s Detection Using PCA-Compressed CNN Features
Main Article Content
Abstract
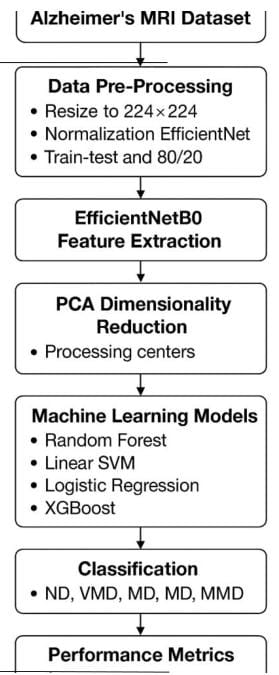
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, and its early identification is critical for timely clinical intervention. Deep learning models achieve strong performance in medical image analysis but often require high computational resources, limiting deployment in low-resource environments. This study proposes a lightweight hybrid framework that integrates deep feature extraction using EfficientNetB0 with traditional machine learning classifiers for multiclass Alzheimer’s disease classification. MRI images from the Alzheimer’s Multiclass Equal and Augmented Dataset were processed using an EfficientNetB0 feature extractor, and the resulting high-dimensional feature vectors were compressed using Principal Component Analysis (PCA) to reduce memory footprint and training time. Four machine learning classifiers—Random Forest, Linear SVM, Logistic Regression, and XGBoost—were trained and evaluated on the compressed features. Experimental results show that the hybrid approach achieves competitive performance, with XGBoost obtaining the highest accuracy of 75%, followed by Linear SVM at 74%. The results demonstrate that PCA-compressed deep features combined with classical ML models provide an efficient and scalable solution for multiclass Alzheimer’s diagnosis while maintaining low computational complexity. This framework is particularly suitable for real-world clinical applications where computational resources are limited.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.